I. Introduction
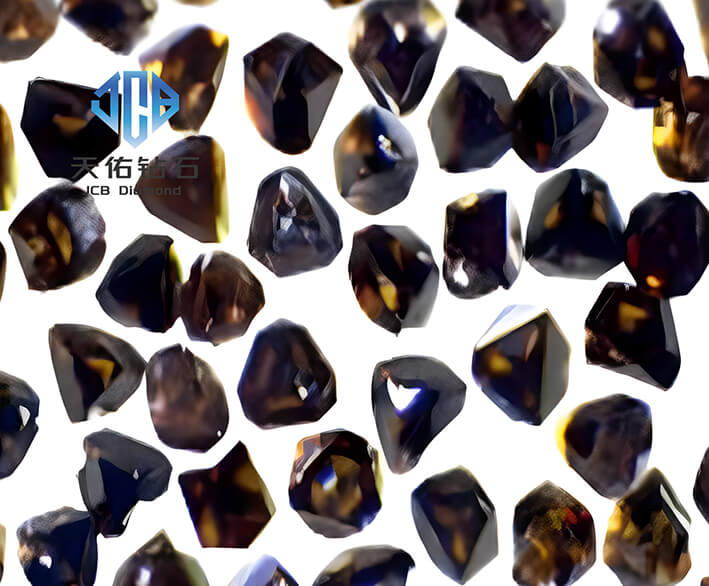
Cubic boron nitride (cBN) single crystal, as a superhard material, plays an extremely important role in industrial processing, cutting tools, grinding tools and other fields. Its unique physical and chemical properties make it one of the hot spots in modern materials science research. This report aims to deeply explore the structure, performance, preparation method, application status, challenges and future development trends of cubic boron nitride single crystal.
II. Structure and properties of cubic boron nitride single crystal
(I) Crystal structure
Cubic boron nitride has a sphalerite structure similar to diamond, in which boron atoms and nitrogen atoms are arranged alternately with covalent bonds to form a face-centered cubic lattice. This structure gives cubic boron nitride the characteristics of high hardness, high wear resistance and high stability.
(II) Physical properties
Hardness: The hardness of cubic boron nitride is second only to diamond, and its Vickers hardness can reach 45-50 GPa, which enables it to effectively process various high-hardness materials such as steel, cemented carbide, etc.
Thermal stability: In high temperature environment, cubic boron nitride shows good thermal stability and can remain stable in the temperature range of 1200-1500°C. This feature gives it a unique advantage in high-speed cutting and high-temperature processing.
Thermal conductivity: It has a high thermal conductivity, which helps to dissipate heat in time during processing, reduce tool wear and thermal deformation of workpieces.
Optical properties: It has good optical transmittance within a certain wavelength range and can be used in optical coatings, window materials and other fields.
(III) Chemical properties
Cubic boron nitride has relatively stable chemical properties, has certain corrosion resistance, and is not easy to react chemically in general acid and alkali environments. However, under high temperature, high pressure and the presence of certain specific chemicals, chemical reactions may occur, affecting its performance.
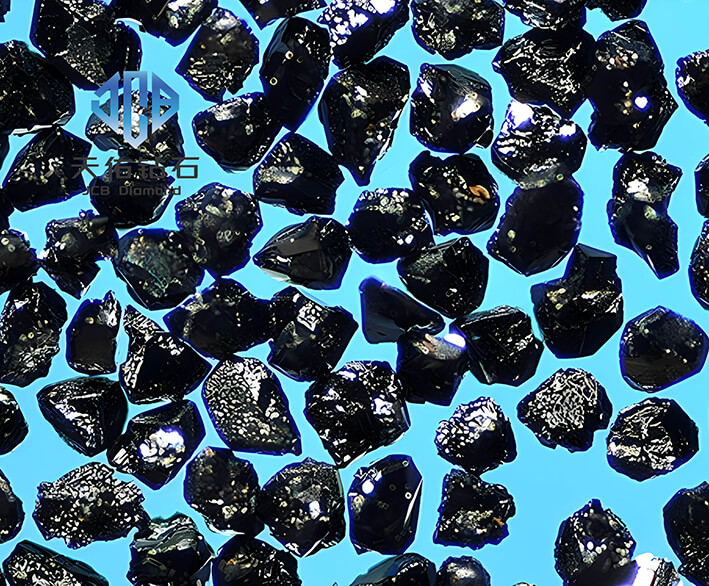

III. Preparation method of cubic boron nitride single crystals
(I) High temperature and high pressure synthesis method
This is one of the main methods for preparing cubic boron nitride single crystals. Usually, under high temperature (1200 - 2000°C) and high pressure (4 - 8 GPa), hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) is used as raw material, metal catalysts (such as lithium, magnesium, sodium, etc.) are added, and cubic boron nitride single crystals are synthesized through phase change reaction. This method can produce large-sized, high-quality cubic boron nitride single crystals, but the equipment is expensive, the process is complicated, and the energy consumption is high.
(II) Chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
The gaseous boron-containing and nitrogen-containing compounds are used to react chemically under high temperature, low pressure and plasma auxiliary conditions to deposit cubic boron nitride single crystals on the substrate surface. This method can accurately control the crystal growth process and the thickness and quality of the film, and can produce nano-scale cubic boron nitride films or crystals, but the growth rate is relatively slow, and it is difficult to obtain large-sized bulk single crystals.
(III) Other methods
Such as pulsed laser deposition and self-propagating high temperature synthesis, they are also used in the preparation of cubic boron nitride single crystals, but they are still in the stage of laboratory research or small-scale trials, and have not yet achieved large-scale industrial production.
IV. Application status of cubic boron nitride single crystals
(I) Cutting tool field
Cubic boron nitride tools are widely used in metal cutting, especially for the processing of hardened steel, heat-resistant alloys, titanium alloys and other difficult-to-process materials with high hardness. Compared with traditional carbide tools, cubic boron nitride tools have higher cutting speeds, longer tool life and better processing surface quality, which can significantly improve processing efficiency and reduce processing costs.
(II) Grinding tool field
Grinding tools such as grinding wheels and belts made of cubic boron nitride abrasives perform well in grinding. They can be used to grind high-speed steel, mold steel, bearing steel and other materials, and can achieve high-precision and high-efficiency grinding. The heat generated during the grinding process is small, and it is not easy to burn the workpiece surface.
(III) Other fields
In the electronics industry, cubic boron nitride can be used to prepare heat dissipation substrates for high-temperature, high-power semiconductor devices; in the optical field, it can be used as a high-hardness, high-refractive-index optical window material and coating material, and is applied to infrared optical systems, laser optical systems, etc.; in the field of oil drilling, cubic boron nitride drill bits can improve drilling efficiency and drill bit life, and adapt to the drilling needs of complex formations.
V. Challenges and future development trends faced by cubic boron nitride single crystal research
(I) Challenges faced
High preparation cost: Whether it is high-temperature and high-pressure synthesis method or chemical vapor deposition method, there are problems such as large equipment investment, high raw material cost, and high energy consumption, which leads to high preparation cost of cubic boron nitride single crystals, limiting its wider application.
Crystal quality control: In the large-scale preparation process, it is difficult to accurately control the crystal structure integrity, internal defects, impurity content, etc. of cubic boron nitride single crystals, which will affect the performance and application effect of the crystal.
Preparation of large-size single crystals: Although the high-temperature and high-pressure synthesis method can produce large-size single crystals, as the size increases, the quality uniformity and stability of the crystals are difficult to guarantee; and the preparation of large-size bulk single crystals by chemical vapor deposition still faces many technical difficulties.
(II) Future development trends
Innovation in preparation technology: Develop new synthesis methods or improve existing processes to reduce preparation costs and improve crystal quality and production efficiency. For example, explore new catalysts or fluxes to optimize the high-temperature and high-pressure synthesis process, and develop new gas sources and reaction devices to increase the growth rate and crystal size of the chemical vapor deposition method.
Expanding application areas: With the continuous advancement of science and technology, cubic boron nitride single crystals are expected to be used in emerging fields such as quantum computing, new energy materials, and aerospace. For example, its stability in extreme environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and strong radiation makes it possible to become a potential substrate material for quantum chips.
Compounding and functionalization: Develop cubic boron nitride-based composite materials or functional materials with a variety of excellent properties by compounding with other materials or performing functionalization design. For example, composite materials of cubic boron nitride and metals, ceramics, etc. are prepared to achieve an organic combination of high strength, high toughness and high hardness of the material; cubic boron nitride materials with special functions such as self-lubrication, antibacterial, and photoelectricity are developed.
In summary, cubic boron nitride single crystal, as an important superhard material, has broad application prospects and great research value. Although there are still some challenges in preparation and application, with the continuous innovation and development of science and technology, it is expected to play a key role in more fields in the future and promote the progress of related industries.
